Heat recovery is essential in industrial applications and Foundries as significant waste heat is generated from furnaces, kilns, boilers, and exhaust systems during heat-intensive industrial processes such as melting, forming, smelting, refining, casting, vulcanization, extrusion, solvent evaporation, drying, polymerization and curing.
However, Glass, metal, paint, polymer & rubber manufacturing industries face heat recovery challenges such as the presence of particulate matter, fumes and corrosive gases in exhaust streams, variable air stream compositions, and the need for consistent temperature control to ensure product quality. Airborne particles generated during manufacturing processes can accumulate on heat exchanger surfaces, leading to fouling and reduced heat transfer efficiency.
Managing polluted emissions while recovering heat is a complex challenge. Additionally, manufacturing processes vary widely depending on the product being produced, the raw materials used, and the production scale. Implementing heat recovery in highly specialized processes pose challenges and require custom-engineered solutions.
This is where Lepido shines.
Lepido' captures high-temperature waste heat which can be reused in customized ways to reduce gas consumption and operational costs. Its patented coil geometry allows particles and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) to pass through without clogging and maintaining high heat transfer efficiency.
.png?width=1200&height=627&name=Without%20energy%20recovery%20(2).png)
Lepido is resilient against pollutants like lint, moisture, particles and fibers and is suitable for diverse manufacturing applications as it seamlessly integrates into a Run-Around-Circuit, overcoming the Coanda effect.
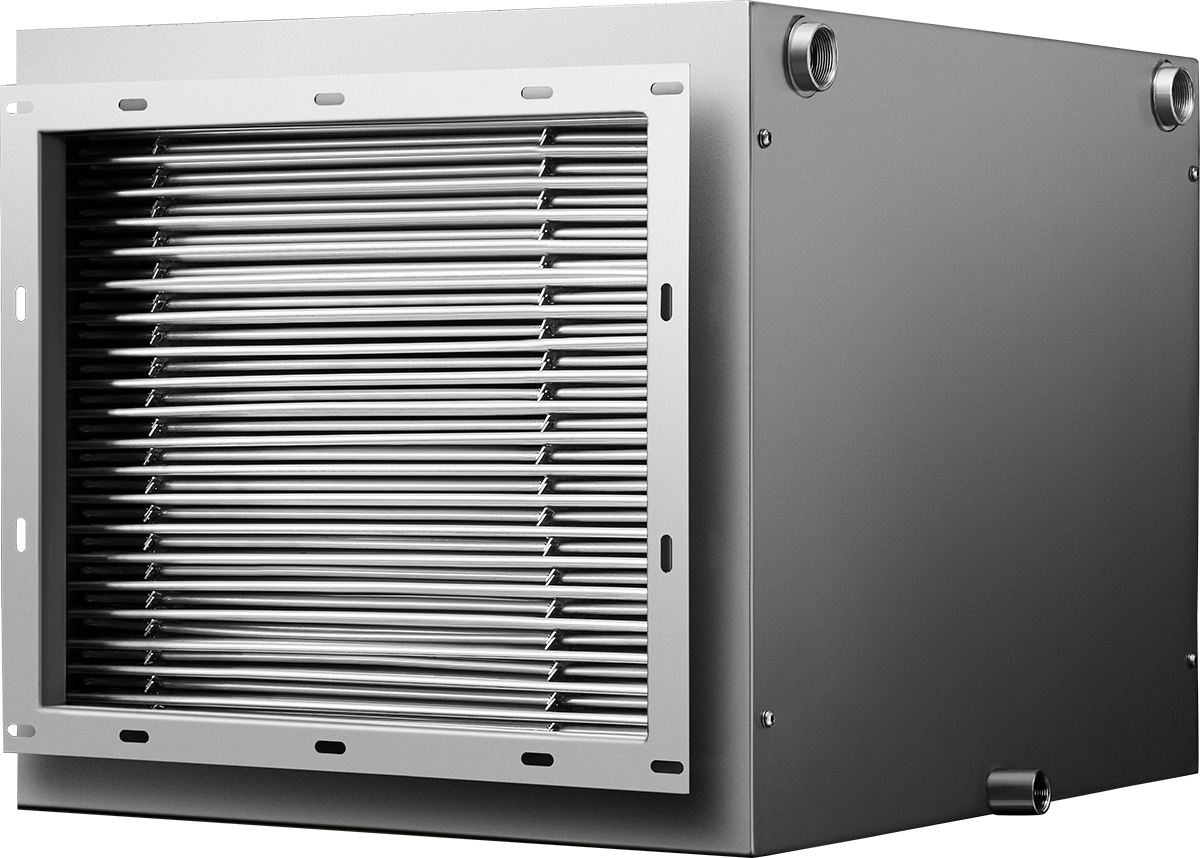

Its patented robust construction, resistance to contaminants, and ability to handle high temperatures, pressure and variable air streams make it an ideal solution for industrial heat recovery applications. The recovered heat can be used to heat replacement air or returned to the process itself by preheating liquid/air.
By recovering waste heat instead of burning additional fossil fuels, facilities can reduce their energy bills and operational costs, enhance their competitiveness and lower their carbon footprint.
.png?width=1200&height=1200&name=Copy%20of%20Segment%20till%20hemsida%20(8).png)
Success Story: At a polymer manufacturing facility operating for 11.4 hours per day in Belgium that produced artificial grass for sports applications, our technology recaptured heat from an exhaust air flow of 2.4m³/s at 90°C. This resulted in annual energy savings of 441,066 kWh, annual monetary savings of €23,900, and a reduction of 110 tons of CO2 emissions per year.
-1.png?width=1200&height=1200&name=Client%20portfolio%20(2)-1.png)